Customer Experience: Automation of Experiences
Features
- It is an administration interface
Screens
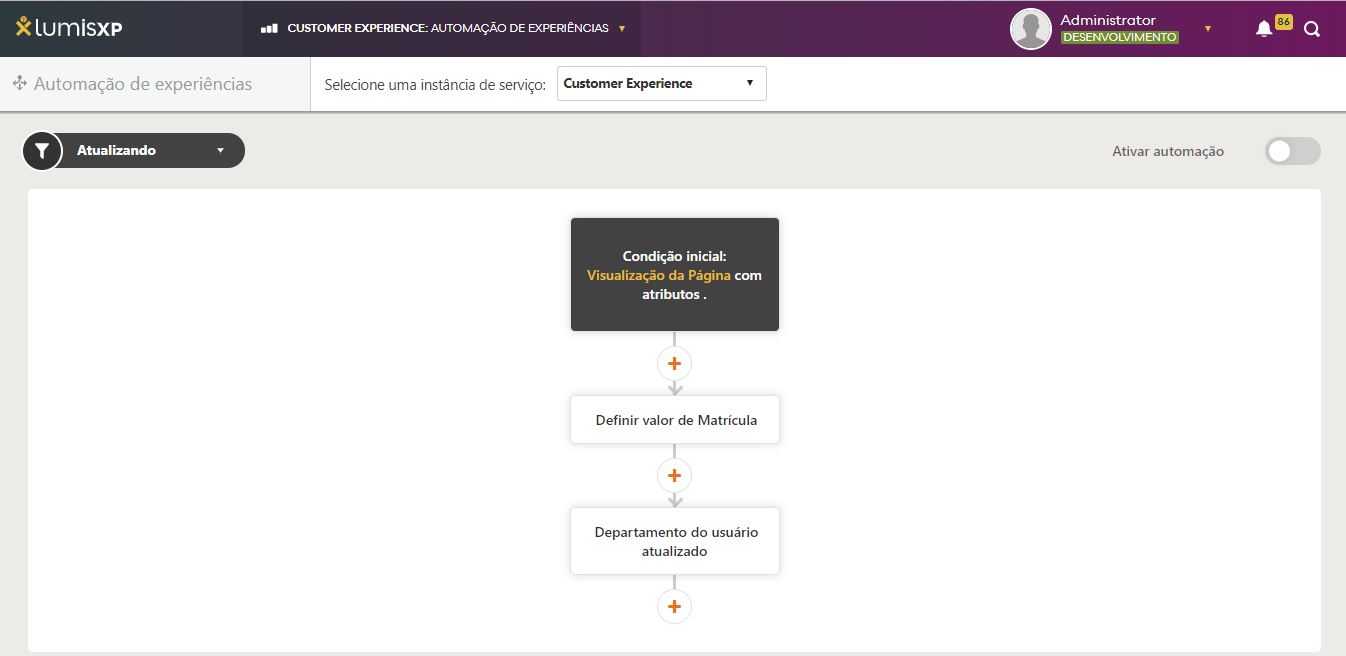
Functionality Concepts:
The experience automation functionality allows publishers to automate tasks to improve their customers' experience.
This automation is done through execution flows created by the publishers. These flows aim to make decisions and execute actions autonomously to
enhance user experience.
Based on the events occurring on the platform (page views, for example), the framework decides which flows should be executed and executes them.
First, the publisher must define which action will trigger the flow. This action is the filter that determines whether the flow should be executed for an event that
is happening on the platform.
Once the publisher has defined the entry action, they can continue to build the experience automation flow using the available elements.
For example, suppose the scenario of a shopping mall website where one wants to enhance the user experience to help them pay for their parking
directly through the website.
Suppose that in order to pay for their parking they must follow these steps:
- Enter the parking payment page
- Scan the barcode of the parking ticket
- Make the payment
parkingPaymentStatus of type Identifier will be created.
This attribute can have one of the following values:
- No value: indicates that the user did not attempt to make the payment. In this case, we can show an eye-catching banner to encourage the user to enter the payment page.
-
enteredpayment: indicates that the user entered the payment page but could not proceed. In this case, a flashy banner can be shown with instructions on how to scan the barcode using the phone camera. -
scannedticket: indicates that the user scanned the ticket but did not make the payment. In this case, a flashy banner can be shown with instructions on how to make the payment.
-
Users who did not attempt to make the payment: this segment could, for example, be defined as "users who do not have a value in the
parkingPaymentStatusattribute." -
Users who did not scan the barcode: this segment could, for example, be defined as "users who have the value 'enteredpayment'
in the
parkingPaymentStatusattribute." -
Users who did not make the payment: this segment could, for example, be defined as "users who have the value 'scannedticket'
in the
parkingPaymentStatusattribute."
The following events will also be created:
enteredpayment: this event will be triggered whenever the user enters the parking payment page.scannedticket: this event will be triggered once the user manages to scan the barcode of the ticket.madepayment: this event will be triggered once the user manages to make the parking payment.
In this situation, the publisher could create an experience automation flow to assist these users.
The first flow would be to add the value
enteredpayment to the parkingPaymentStatus attribute of the user,
once an enteredpayment event is detected.
This flow could have the following definition:
-
Entry action: Events of type
enteredpayment. -
Filter by segmentation: User does not have a value for the
parkingPaymentStatusattribute (only passes through the flow those users who do not yet have a value for the attribute). -
Add user attribute: Attribute:
parkingPaymentStatusvalueenteredpayment. - Recalculate segmentations: Segmentations: "Users who did not attempt to make the payment" and "Users who did not scan the barcode."
parkingPaymentStatus from enteredpayment to
scannedticket, when the user manages to scan the ticket.
This flow could have the following definition:
-
Entry action: Events of type
scannedticket. -
Filter by segmentation: User has the value
enteredpaymentin theparkingPaymentStatusattribute. -
Add user attribute: Attribute:
parkingPaymentStatusvaluescannedticket. - Recalculate segmentations: Segmentations: "Users who did not scan the barcode" and "Users who did not make the payment".
parkingPaymentStatus attribute, once the user manages to make
the payment.
This flow could have the following definition:
-
Entry action: Events of type
madepayment. -
Filter by segmentation: User has the value
scannedticketin theparkingPaymentStatusattribute. -
Remove user attribute: Attribute:
parkingPaymentStatus. - Recalculate segmentations: Segmentations: "Users who did not make the payment" and "Users who did not attempt to make the payment".
Types of flow elements:
- Filter by event attributes
- It is a filter used to filter the event by its attributes. If the event in question does not match the filter, the flow ends.
- Filter by user segmentation
- It is a filter used to filter the events performed by users of a specific segmentation. If the event is not performed by a user (system events, for example) or if the user who performed the event does not match the defined filter, the flow will end. In this filter, it is possible to create a new segmentation or choose an existing segmentation.
- Define user attribute value
- Action that defines the value of a user attribute for the user who performed the event. If the event does not have a user, an error will be generated, and the flow will end. If the user already has the attribute, it will be replaced by the defined value.
- Remove user attribute
- Action that removes a user attribute from the user who performed the event. If the event does not have a user, an error will be generated, and the flow will end.
- Recalculate user segmentations
- Action that recalculates selected user segmentations for the user who performed the event instantaneously, meaning it removes the user from the segmentation if the filter no longer accepts this user or adds this user to the segmentation if the filter of this segmentation accepts this user.
- Execute a custom action
- Action that executes custom code. The code must have been previously developed by the solution's developers. This action has a single configuration, which is the name of a Java class that must be executed. This Java class implements the interface ICustomAction. For technical information on how to implement a custom class, see the JavaDoc of the mentioned interface.
- Wait in the automation flow
- Action that suspends the automation flow for a time defined by the user. When the time is up, the automation flow will continue to execute at the next step. You can choose how many minutes, hours, and days to wait.
- Wait for event
-
Action that temporarily suspends the automation flow until a certain event is executed. You can specify additional filters for the event.
For example, the event must also have been performed on a specific page.
It will be necessary to define an expiration period for the wait for the event. If this period is exceeded, the flow will proceed to the expiration path. - Add user to the journey
-
Action that adds the user who executed the event to a stage of the journey. Both the journey and the
stage must be registered in advance in the Journeys mode. The stage must be of type
journey start.
If the user is already in the journey at any stage when the event is executed, the action of the node will not be executed, and the flow will end. - Move user in the journey
-
Moves the user who executed the event to another stage of the journey. Both the journey and the stage must be registered in advance in the
Journeys mode. If the stage is of type
journey end, the user will automatically be removed from the journey.
If the user is already at the destination stage of the journey when the event is executed, the action of the node will not be executed, and the flow will end. The same happens if the user is not in any stage of the journey. - Remove user from the journey
-
Removes the user who executed the event from the journey. The journey must be registered in advance in the
Journeys mode.
If the user is not already in the journey when the event is executed, the action of the node will not be executed, and the flow continues its execution.
Permissioning
- Manage Experience Automations: Allows access to the Experience Automation mode to manage existing automations.